Scientists have created a durable and flexible alloy using 3D printing
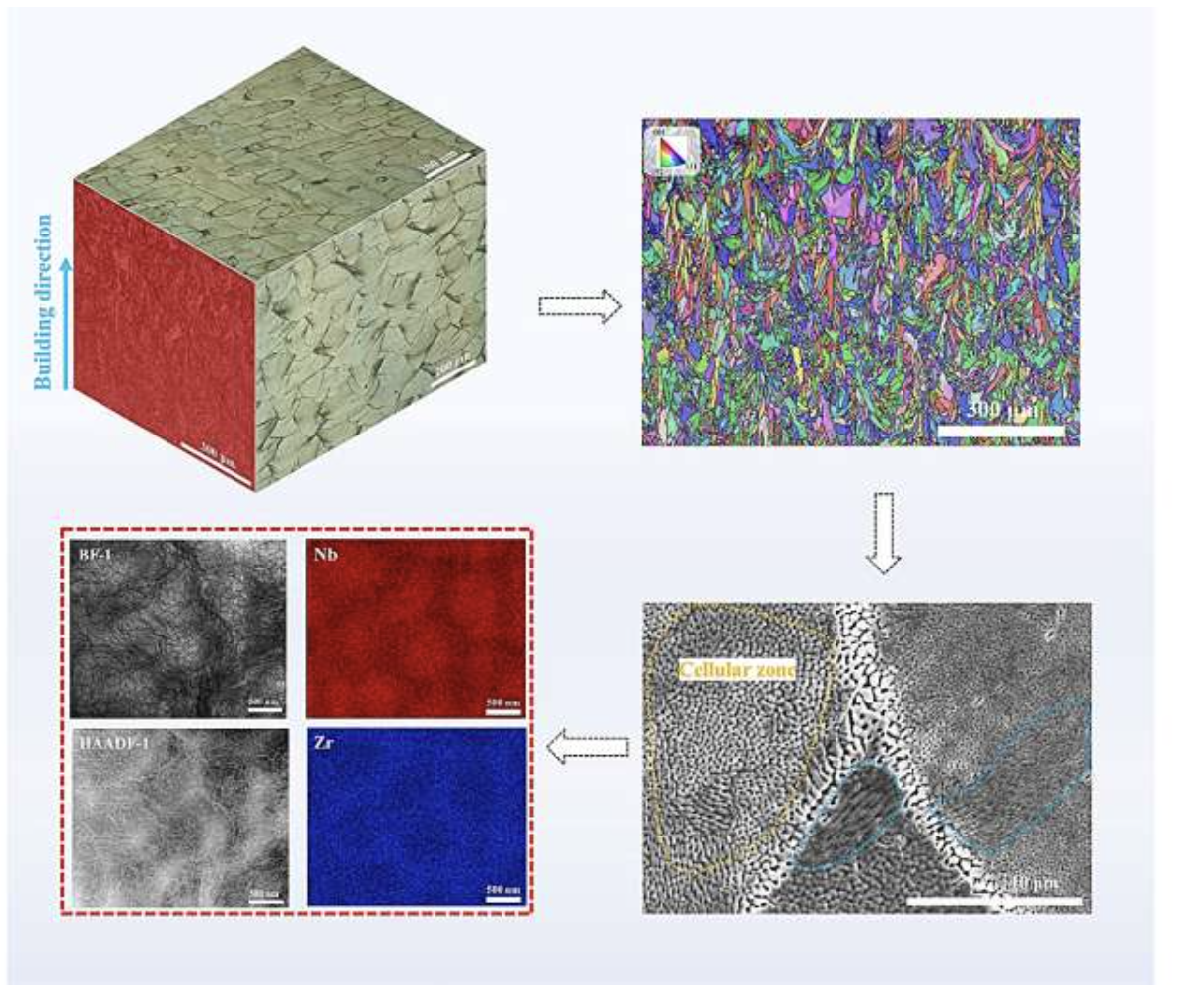
A team of scientists from universities in China and Singapore have developed a unique alloy that combines strength and flexibility using 3D printing technology. This material, called NTZO, is composed of niobium, titanium and zirconium with the addition of oxygen and is created using laser powder sintering (L-PBF). Rapid heat treatment during the printing process imparts properties to the alloy that make it suitable for use in the most demanding environments such as aerospace and medicine.

New alloys based on refractory metals are often strong but not flexible enough, which limits their use. However, during the 3D printing process, scientists added a little oxygen to the composition, which improved both the strength and flexibility of the material. This combination of important properties is especially valuable for materials that must withstand significant loads without breaking.
The 3D printing method used to create NTZO promotes the formation of a special microstructure in which metal particles are randomly positioned and improves the mechanical properties of the alloy. This approach gives researchers the ability to precisely control the structure of materials, opening up new perspectives in metal processing.
The results of this work could find application in the production of parts for the aerospace industry, medical implants and other products with high durability and resistance to harsh conditions. harshness is important. In the future, the researchers plan to continue studying the influence of thermal cycling on the properties of alloys in order to improve the technology for creating such materials and expand their applications in engineering.
 © Yaqiong An, Jun Ding at Xi'an Jiaotong University
© Yaqiong An, Jun Ding at Xi'an Jiaotong University




Leave a Reply